Testing Robot Challenge
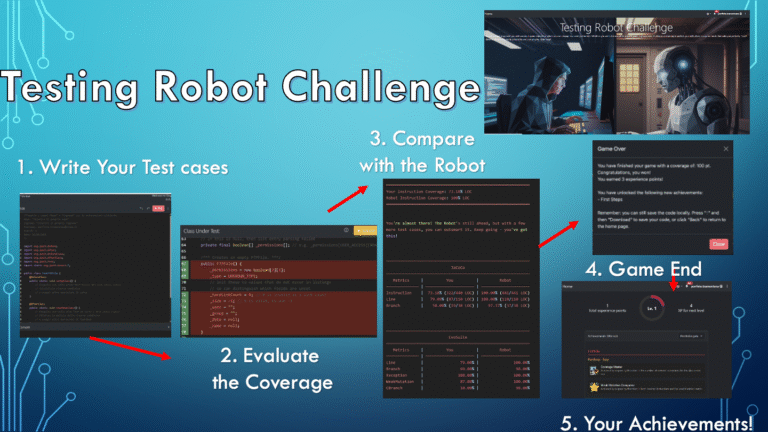
TestingRobotChallenge is a Web application designed to support the learning of software testing through gamification, where players compete against preconfigured tester opponents called Robots. The goal for each player is to write JUnit4 test code for a given Java class, aiming to outperform — or at least match — the effectiveness of the test cases automatically generated by the opponents. Successful players are awarded scores and achievements for each challenge they win. A leaderboard tracks player performance, showing the number of challenges won and the total score earned. Top-performing players are eligible for rewards.
Learning Objectives of the Web App:
- Motivate students to practice software testing exploiting the gamification
- Learn how to write effective unit tests with a focus on code coverage
- Allow students to acquire familiarity with existing test automation tools.
TestingRobotChallenge is realized in the context of the ENACTEST Erasmus+ project (https://enactest-project.eu/) financed by the European Commission (Project Number 101055874) and by the GATT project financed by the University of Naples Federico II.
Testing Robot Challenge is used by students of Software Engineering and Software Testing courses
It is available at : https://github.com/reverse-unina/TestingRobotChallenge
It is also currently evolved by students of Software Archictecture Design course. The development version is available at : https://github.com/Testing-Game-SAD-2023/A13
Test Smell Game (TSGame)
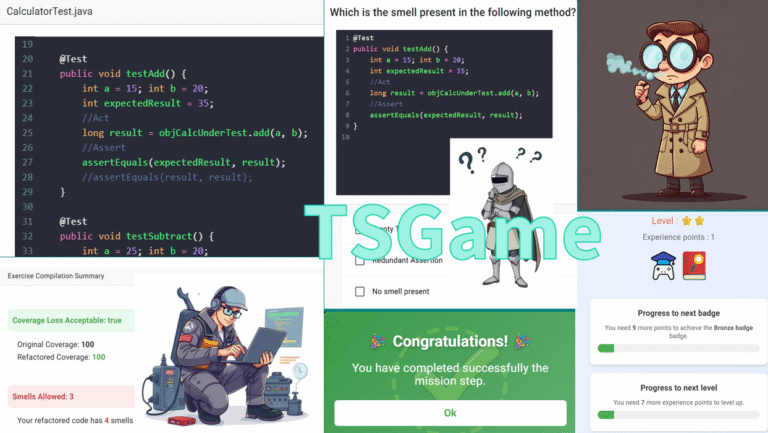
The presence of test smells related to low-quality test cases is a known factor contributing to problems in maintaining both test suites and production code. The TSGame (Test Smell Game) capsule provides a serious game where students can familiarize with test smells by practicing with their detection and removal from JUnit test code. TSGame has been implemented as a Web-based application that allows a teacher to assign students test smell detection and refactoring tasks that they have to accomplish in game sessions. Upon completion of the tasks they have the possibility to gain rewards.
TSGame is realized in the context of the ENACTEST Erasmus+ project (https://enactest-project.eu/) financed by the European Commission (Project Number 101055874) and by the GATT project financed by the University of Naples Federico II.
TSGame is actively used by students of the Software Testing course.
TSgame is available at : https://github.com/reverse-unina/TestSmellGame
UnoProcidaResidente

It is a ferry timetable application, used as working example for the Advanced Operating Systems course.
It is available at : https://github.com/reverse-unina/UnoProcidaResidente
FunesDroid
The goal of the FunesDroid tool is to check whether the Activity classes of an analyzed Android app expose or not memory leaks tied to the Activity lifecycle.
FunesDroid is able to execute automatically the following test on the input apks:
- Double Orientation Change (DOC), corresponding to a double rotation of the device, from landscape to portrait and finally to landscape or, equivalently, from portrait to landscape and, finally, to portrait. Each of these orientation changes exercises the EL loop, since the running Activity is destroyed and recreated in order to fit the rotated device layout.
- Background-Foreground (BF), corresponding to a sequence of events exercising the VL loop. For example, a possible sequence includes the click on the Back button of the device (that may bring the running Activity to the Stopped state), followed by the selection of the same Activity from the list of the recently stopped one. This last event causes the restarting of the Activity, without the need to redraw its graphical layout.
- Semi-Transparent Activity Intent and back (STAI), corresponding to a sequence of events exercising the VL loop. This sequence bring the running Activity to the paused state, and successively to the running state.
The three considered lopps are the following:
- Entire Loop (EL) of an Activity consists in the Resumed-Paused-Stopped-Destroyed-Created-Started-Resumed sequence of states. This loop can be exercised by events that cause a configuration change, e.g. an orientation change of the screen, that destroys the Activity instance and then recreates it according to the new configuration;
- Visible Loop (VL) corresponds to the Resumed-Paused-Stopped-Started-Resumed sequence of states during which the Activity is hidden and then made visible again. There are several event sequences able to stop and restart an Activity, e.g. turning off and on the screen or putting the app in background and then in foreground again through the Overview or Home buttons;
- Foreground Loop (FL) of an Activity involves the Resumed-Paused-Resumed state sequence. The transition Resumed-Paused can be triggered by opening non full-sized elements such as modal dialogs or semi-transparent activities that occupy the foreground while the Activity is still visible in background. To trigger the transition Paused-Resumed the user should discard this element.
FunesDroid is available at : https://github.com/reverse-unina/FunesDroid
AndroidRipper
AndroidRipper is a toolset for the automatic GUI testing of mobile Android Applications.
It is developed and maintained by the REvERSE (REsEarch laboRatory of Software Engineering) Group of the University of Naples "Federico II".
It is available at : https://github.com/reverse-unina/AndroidRipper
EXACT

EXcel Applications Comprehension Tool.
It is an Excel 2010 Addin providing support for comprehension tasks of Excel Applications.
It is available here: https://github.com/reverse-unina/EXACT






